East Meets West Acupuncture offers non-invasive and affordable facial rejuvenation and holistic whole-body wellness to the greater Kansas City area.
East Meets West Acupuncture Kansas City is a supportive sanctuary for clients to restore their glow, vibrancy, and confidence.
Brandi offers a wide range of natural and effective tools and therapies that blend Eastern medicine with Western practices for a healthy and vibrant mind, body, and spirit.
Hi, I’mBrandi West
Licensed Acupuncturist specializing in helping you look and feel great in all seasons of life.
Learn more about Brandi West’s background and experience, as well as her approach to aging, stress management, and mental health.
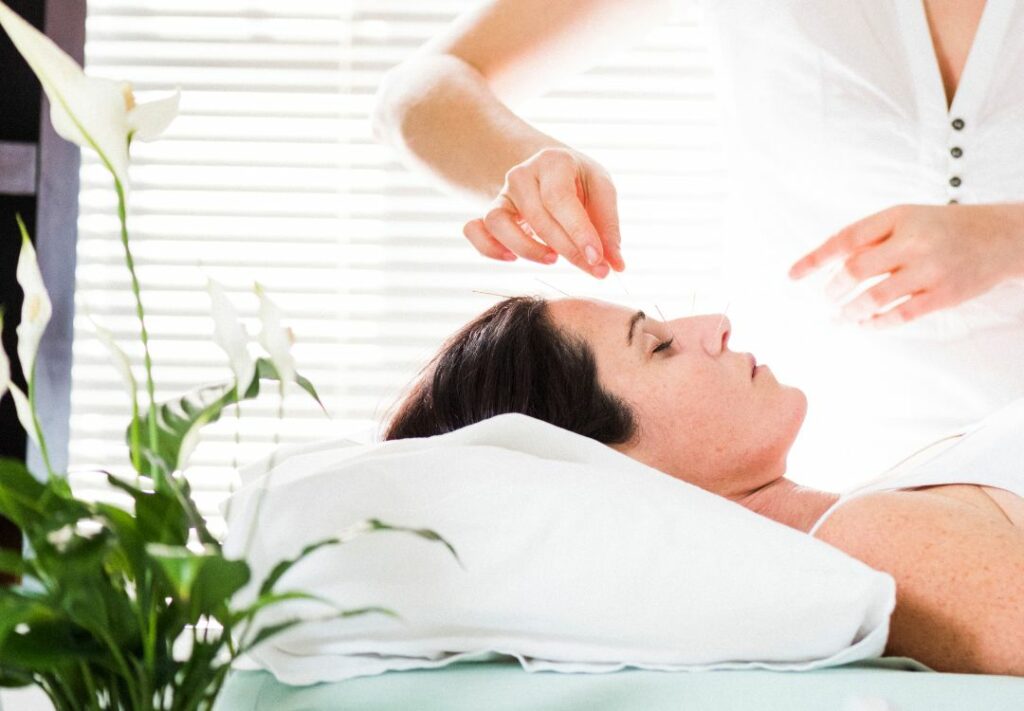


Want to find out if you are a good candidate for Facial Rejuvenation?
Click the link below to schedule a 15-minute complimentary phone consultation with Brandi West.
Explore our services
Patient Love
"After visiting Brandi my mental health has significantly improved and has kept my anxiety and depression in check. Brandi’s compassion, knowledge, and skills have been a game changer for my overall wellbeing!"
A.M.
“I was diagnosed with ulcerative colitis 10 years ago and after taking prescribed medicine for many years and putting up with side effects that were worse than the condition itself, I decided to explore other options. I reached out to the Pacific College of Oriental Medicine in San Diego, and Brandi West was recommended to me. After my first session, Brandi had a good understanding of my condition, made me feel like a person, instead of a patient, and she developed a life plan suited just for me that taught me to understand both my body and my condition. I felt under more care with Brandi than I have ever felt with any other healthcare provider, and the results were both uplifting and fulfilling!”
T. Schultz
“I’ve had pain in my neck and shoulder for a long time. My massage therapist suggested I try acupuncture many months ago. I was very nervous about it and then I met Brandi. She put my mind at ease at our first appointment. She asked me tons of questions and then explained everything she was doing to treat me. The first treatment made a big difference and all subsequent treatments have added to my well-being. I’m very glad that Brandi moved to KC!”
E. Duke
“My experience with Brandi has been amazing! She’s an excellent acupuncturist and goes above and beyond for her patients. One thing that sets her apart from other doctors and practitioners is that she really takes the time to listen. We have a conversation every time I see her and she always provides great advice and suggestions that compliments the acupuncture treatments. She can really pinpoint the exact area that needs work and I always feel so much better when we’re done. Brandi has such an energetic personality and positive attitude, which creates the perfect environment and experience every time I see her. I highly recommend Brandi for acupuncture!”
Heather L.
“A year after falling during a run and bouncing my head against the asphalt path, I was still experiencing headaches, lightheadedness and occasional dizziness. It was recommended I try acupuncture and that was when I was introduced to Brandi at East Meets West Acupuncture. I had never had acupuncture before and really knew nothing about it. In scheduling my first appointment I saw that it took 90 minutes, and that turned out to be the best 90 minutes I have taken to help my symptoms. During my first session with Brandi, she took the time to get to know me, my past health issues, and more importantly my current conditions. She explained what to expect and how the treatment would help. After following Brandi’s prescribed treatment plan, my symptoms subsided and I’m happy to report I have not had a headache in over a year.”
Chuck P.
Previous
Next